Who Is an Agile Business Analyst?
In the modern era, where agility and adaptability have become more important than ever for businesses, the role of an Agile Business Analyst has grown exponentially in importance.
Unlike traditional business analysts, who often function within the boundaries of structured, phase-based projects, the Agile Business Analyst is the epitome of adaptability.
They work in fast-paced, frequently changing Agile environments, collaborating closely with development teams and stakeholders to deliver incremental improvements to products and services.
This blog post aims to dissect the role, responsibilities, and significance of an Agile Business Analyst.
Understanding Agile

Understanding Agile is foundational to appreciating the role of an Agile Business Analyst.
Agile is not just a methodology; it’s a mindset that promotes flexibility, collaboration, and responsiveness to change.
In contrast to traditional project management methodologies like Waterfall, where each phase is sequential and largely immutable, Agile adopts an iterative approach.
This involves breaking the project into smaller, manageable pieces known as “sprints,” usually lasting two to four weeks.
Each sprint aims to produce a potentially shippable product increment, providing an opportunity for customer feedback.
This enables the Agile Business Analyst, along with the team, to adapt and improve the product continually.
The Agile framework places a strong emphasis on collaboration among cross-functional teams, which include developers, designers, and business stakeholders.
Herein lies the crux of the Agile Business Analyst’s role—they act as a conduit between the technical team and the business stakeholders, ensuring that both parties are aligned in their objectives and that the product being developed meets the business needs while remaining flexible to change.
Therefore, for an Agile Business Analyst, understanding Agile methodologies is not merely about knowing the ceremonies or artifacts like the sprint or backlog.
It’s about ingraining the Agile philosophy in their approach to problem-solving and requirement gathering, thereby adding value to the product and the business alike.
The Conventional Business Analyst Vs. Agile Business Analyst

The traditional Business Analyst often works on Waterfall projects, where the project phases are linear and do not overlap. In contrast, the Agile Business Analyst operates in a flexible, collaborative environment where changes can be made mid-course without throwing the whole project off track.
Core Responsibilities
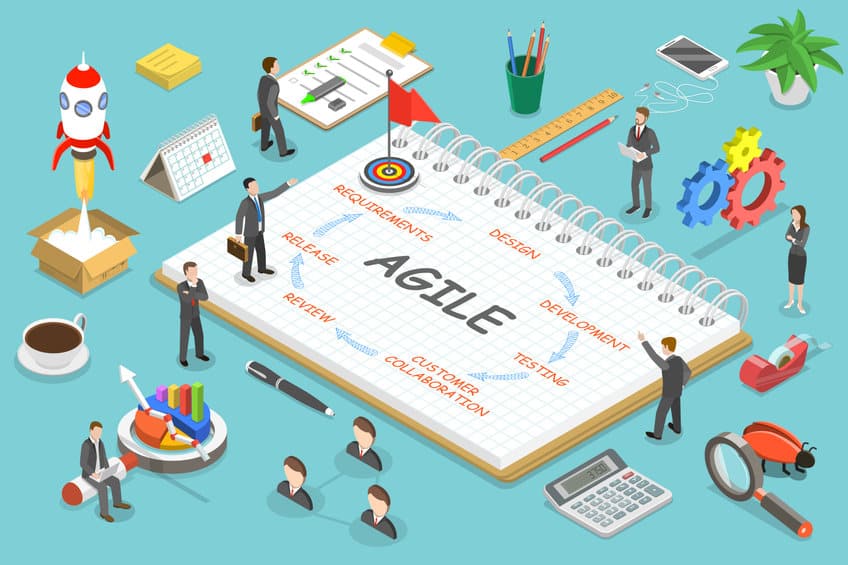

Understanding the core responsibilities of an Agile Business Analyst is crucial for the successful implementation of Agile projects.
These responsibilities encompass various domains, each crucial in its own right.
1. Backlog Management:
One of the key tasks for an Agile Business Analyst is managing the product backlog.
The backlog is a dynamic list of features, enhancements, and bug fixes that are crucial for the product.
The Agile Business Analyst meticulously breaks down complex user stories into more manageable tasks, prioritizing them based on their business value and stakeholder input.
This ensures the development team is working on items that bring the most value to the project.
2. Requirement Gathering:
Unlike traditional models where requirements are gathered upfront, in Agile, this is a continuous, iterative process.
The Agile Business Analyst works in close proximity with stakeholders to consistently update functional and non-functional requirements.
The agility of this role enables the team to pivot based on feedback and emerging needs.
3. Facilitation:
The Agile Business Analyst is often the facilitator during various Agile ceremonies, such as daily stand-ups, sprint planning, and sprint retrospectives.
Their role is to ensure that conversations are productive, and focused and that actionable insights emerge from these gatherings.
4. Quality Assurance:
Quality is not an afterthought in Agile; it’s a continuous focus. The Agile Business Analyst collaborates with the Quality Assurance team to ensure that the features delivered meet the predefined standards and stakeholder expectations.
5. Stakeholder Communication:
One of the most critical responsibilities is keeping open lines of communication between the development team and the stakeholders.
This role ensures that everyone involved understands the project’s progress, what challenges are being faced, and what successes have been achieved.
In doing so, the Agile Business Analyst ensures that the project remains in line with business objectives.
In essence, the Agile Business Analyst acts as a linchpin within the Agile framework, a bridge that ensures both the development team and stakeholders are aligned and that the project delivers real business value.
Skills and Toolset

The skill set and tools required for an Agile Business Analyst are both specialized and versatile, encompassing a range of proficiencies designed to adapt to the dynamic nature of Agile projects.
Firstly, understanding Agile frameworks such as Scrum or Kanban is crucial. These frameworks guide the way an Agile Business Analyst interacts with both the development team and stakeholders, defining the processes for how tasks are planned, executed, and reviewed.
Strong communication skills are also indispensable. Given the need for continuous interaction with team members and stakeholders, an Agile Business Analyst must be able to articulate ideas clearly, understand concerns effectively, and facilitate conversations that lead to actionable solutions.
Backlog management is another essential skill, and familiarity with tools like Jira can be highly beneficial.
The product backlog is the central repository for all tasks in an Agile project, and effective backlog management ensures that the team works on the most valuable tasks at the right time.
Moreover, Agile Business Analysts should be skilled in crafting user stories and defining acceptance criteria, which act as guidelines that the development team can follow.
These are often framed from the user’s perspective and serve as simplified explanations of a requirement, making it easier for developers to understand and implement.
Additionally, the Agile Business Analyst often employs business process modelling tools to visually represent workflows and data interactions.
Data analysis software can also be part of their toolset, aiding in evaluating the project’s impact and identifying areas for improvement.
In summary, the Agile Business Analyst brings a multifaceted skill set to the table, coupling their expertise in Agile methodologies with strong communication skills, a variety of specialized tools, and a keen understanding of both technical and business requirements.
This unique blend ensures that they are a pivotal asset in any Agile project, capable of steering it towards success.
Real-World Applications

Case Study: E-commerce Website
In the realm of e-commerce, enhancing the user experience is a critical factor for success.
Let’s delve into a case study where an Agile Business Analyst plays a pivotal role in upgrading the checkout process of an e-commerce website.
The primary task begins with understanding the users’ needs and identifying their pain points.
To accomplish this, the Agile Business Analyst initiates user interviews and conducts surveys.
Through this research, one significant pain point that emerges is the checkout process; customers desire a quicker and more streamlined experience.
Armed with this vital feedback, the Agile Business Analyst drafts user stories to translate these requirements into actionable items.
An example might be, “As a customer, I want a quicker checkout process so that I can save time.” During the sprint planning meeting, this user story gets high-priority status, given its direct impact on user satisfaction.
To implement this, the Agile Business Analyst collaborates closely with the development team to break down the user story into smaller, manageable tasks, like optimizing form fields or reducing page load times.
As the team works through subsequent sprints, our Agile Business Analyst remains agile—constantly gathering stakeholder feedback and dynamically adjusting the backlog to reflect any newly emerged requirements or insights.
Once the development team has crafted the new checkout feature, the Agile Business Analyst joins forces with the Quality Assurance (QA) team.
Their role here is to guarantee that the changes meet the quality standards and that the new checkout process aligns with the original user story, ultimately ensuring it is both functional and user-friendly.
By guiding the project from initial research to final quality checks, the Agile Business Analyst serves as an invaluable asset, ensuring the e-commerce website’s checkout process is not only enhanced but also directly aligned with the needs and expectations of its users.
Challenges Faced

Navigating the complexities of an Agile environment comes with its own set of unique challenges that an Agile Business Analyst must be prepared to face. Let’s explore some of these hurdles in detail:
1. Scope Creep:
Agile methodologies are iterative by nature, focusing on incremental improvements and quick adaptations to change.
However, this flexibility can sometimes lead to “scope creep,” where the project starts to extend beyond its initial objectives.
Agile Business Analysts must be vigilant in maintaining the focus and integrity of the project scope.
They need to have a robust backlog management strategy in place to ensure that the project doesn’t deviate from its core goals while still benefiting from agile’s adaptability.
2. Stakeholder Resistance:
In traditional environments, stakeholders are often used to a fixed, linear approach to project management. Introducing Agile can meet with resistance from those unfamiliar with its benefits.
An Agile Business Analyst plays a crucial role here, acting as an Agile evangelist. They are responsible for educating and aligning stakeholders about the advantages and efficiencies that Agile methodologies bring to the project.
3. Ambiguity:
Agile projects trade-off detailed long-term planning for the ability to adapt and evolve.
This characteristic can create a level of unpredictability and ambiguity. Agile Business Analysts must be comfortable working in such fluid conditions.
They should be skilled in dynamic problem-solving and able to make informed decisions even when not all variables are known.
Agile Business Analyst needs to be equipped with a unique set of skills and strategies to navigate these challenges successfully.
They must serve as a mediator, educator, and strategic planners, ensuring that the project stays aligned with both its scope and stakeholders’ expectations while thriving in the adaptable world of Agile.
The Agile Business Analyst’s capacity to balance these often-competing demands makes them an indispensable part of any Agile project team.
The Importance of Agile Teams
An Agile Business Analyst is an invaluable asset to Agile teams for several reasons, acting as a versatile bridge that links business goals to technical solutions.
Far from merely gathering requirements or managing tasks, an Agile Business Analyst goes several steps further in facilitating meaningful change.
Firstly, they serve as strategic advisors who can align the technical work being done with broader business objectives.
They are not just concerned with what the Agile team is producing but are keenly focused on why it’s being produced and how it will drive business value. This ensures that the outputs generated don’t merely tick off technical checkboxes but genuinely contribute to the company’s goals.
Secondly, Agile Business Analysts bring a level of adaptability and flexibility that is crucial in Agile environments.
They work closely with stakeholders, development teams, and Quality Assurance personnel to ensure that changing requirements are swiftly and accurately reflected in the product backlog.
Their agile mindset is instrumental in translating quick changes in strategy or customer feedback into actionable tasks.
Thirdly, an Agile Business Analyst is often skilled in various Agile frameworks like Scrum or Kanban, allowing them to seamlessly integrate into different Agile settings.
They understand the rituals, roles, and artefacts unique to these methodologies, making them an integral part of the Agile team.
Lastly, Agile Business Analysts play a role in risk management by identifying any constraints or issues that could obstruct the team’s progress.
By doing so, they help in proactive problem-solving and ensuring a smoother project flow.
Conclusion
The Agile Business Analyst has a pivotal role in modern Agile teams. They offer the unique skill set of understanding both business needs and Agile methodologies, making them invaluable in today’s fast-paced business environments.
With the increasing adoption of Agile frameworks across industries, the demand for skilled Agile Business Analysts is on the rise.
Whether you are looking to become one or hire one, understanding the multifaceted role of an Agile Business Analyst can guide you in making informed decisions.
Their adaptability, skills, and business acumen make them an integral part of any successful Agile team.